The heart, a tireless engine at the core of our circulatory system, stands as a symbol of vitality and well-being. Maintaining a healthy heart is a personal priority and a vital necessity for overall health. The heart’s proper function ensures the efficient circulation of oxygenated blood, influencing our well-being and longevity.
What is an Echocardiogram?
An Echocardiogram, commonly known as an Echo, is a non-invasive imaging test that utilises sound waves to create detailed images of the heart. This diagnostic tool provides valuable information about the heart’s structure, function, and blood flow patterns, aiding in assessing and diagnosing various cardiovascular conditions.
How Echo Works
Echo works on the principle of echolocation, similar to how bats navigate. High-frequency sound waves, inaudible to the human ear, are directed towards the heart. These waves bounce off the heart’s structures, creating echoes captured by a transducer. The transducer converts these echoes into real-time images displayed on a monitor. This allows healthcare professionals to visualise the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels, enabling a comprehensive cardiac health evaluation.
Types of Echocardiograms
Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE) – The most common type, TTE involves placing the transducer on the chest’s surface to obtain images of the heart through the chest wall.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE) – In TEE, a specialized transducer is passed into the oesophagus, providing a close and precise view of the heart’s structures. This method is often used in specific clinical situations requiring a more detailed examination.
Doppler Echocardiogram – This type evaluates blood flow patterns within the heart and blood vessels by measuring the Doppler shift of sound waves. It helps assess the velocity and direction of blood flow, aiding in detecting abnormalities.
Stress Echocardiogram – Combined with exercise or medication to induce stress, this type evaluates the heart’s response under challenging conditions. It is particularly useful in assessing coronary artery disease.
The Echo Procedure
Pre-Test Preparation
Individuals can expect some pre-test guidance before undergoing an Echocardiogram (Echo). This may involve instructions such as avoiding heavy meals, wearing comfortable clothing, and being prepared for the test duration. It’s advisable to inform healthcare providers about existing medical conditions or medications to ensure a smooth testing process.
Application of Gel and Transducer
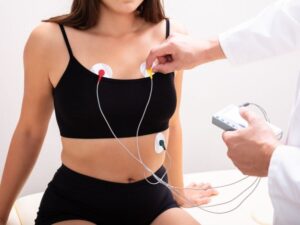
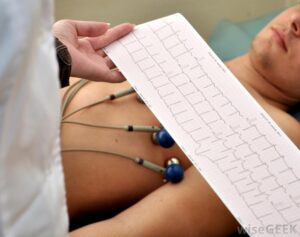
The Echo procedure begins with applying a small amount of gel on the chest. This gel helps ensure optimal contact between the skin and the transducer, a handheld device that emits and receives sound waves. The transducer is then gently moved across different chest areas, capturing high-quality images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels.
Real-time Imaging
As the transducer glides over the chest, it emits sound waves and captures the returning echoes in real time. These echoes are immediately transformed into detailed images displayed on a monitor. Healthcare professionals can simultaneously observe the heart’s structure and function, assessing factors such as chamber size, valve movement, and blood flow patterns. The real-time nature of Echo allows for a dynamic evaluation of the heart, enabling a comprehensive understanding of its performance during the procedure.
Interpreting Echo Results
Understanding Echo Images
Breaking down the visual components of an echocardiogram involves recognising key elements in the images. These include the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels. Understanding the distinctions in grayscale and the use of colour Doppler helps healthcare professionals assess the heart’s structure and function.
Normal vs. Abnormal Findings
Distinguishing between normal and abnormal findings is crucial in echo interpretation. Normal patterns exhibit symmetrical and coordinated movements of the heart’s structures. Abnormalities may manifest as irregularities in chamber size, valve function, or blood flow patterns. Anomalies in these visual cues prompt further investigation into potential cardiovascular issues.
Detecting Heart Conditions
Echo results serve as a powerful diagnostic tool, revealing various heart conditions. Valve disorders, such as regurgitation or stenosis, can be identified by assessing the movement and integrity of the valves. Conditions like heart failure may manifest as changes in chamber size and function.
Congenital heart defects can also be detected by visualising structural abnormalities. The ability of Echo to provide a comprehensive view enables healthcare professionals to detect and diagnose a spectrum of cardiac conditions, guiding appropriate treatment and management strategies.
Common Uses of Echocardiogram
Echocardiograms are versatile diagnostic tools that find applications in various cardiac assessments:
Diagnosing Heart Conditions – Echocardiograms are instrumental in identifying and diagnosing a range of heart conditions, including valve disorders, congenital heart defects, and heart muscle abnormalities.
Monitoring Heart Function – Regular echocardiogram checks help monitor changes in heart function over time. This is particularly important for individuals with known cardiac issues or those undergoing treatment.
Assessing Structural Abnormalities – Echocardiography provides detailed images of the heart’s chambers, valves, and blood vessels, enabling the detection of structural abnormalities that may impact cardiac function.
Guiding Treatment Plans – Healthcare professionals use echocardiogram results to tailor treatment plans for heart conditions, whether through medication, lifestyle modifications, or surgical interventions.
Evaluating Cardiovascular Performance – Stress echocardiograms assess the heart’s response to physical stress, helping evaluate cardiovascular performance and detect issues like coronary artery disease.
Importance of Regular Echocardiogram Checks
Early Detection of Issues – Regular echocardiogram checks facilitate the early detection of cardiac abnormalities, allowing for timely intervention and management. Early detection often leads to more effective treatment outcomes.
Monitoring Progression – For individuals with known heart conditions, routine echocardiograms help monitor the progression of the disease or the effectiveness of ongoing treatments.
Guiding Preventive Measures – Routine echocardiograms can provide insights into an individual’s cardiovascular health, helping healthcare professionals guide preventive measures such as lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, or interventions to reduce the risk of future issues.
Optimising Treatment Plans – By regularly assessing heart function through echocardiograms, healthcare providers can optimise treatment plans, ensuring that interventions are tailored to the individual’s evolving cardiac needs.
Improving Overall Cardiovascular Health – Regular echocardiogram checks contribute to overall cardiovascular health by identifying potential issues before they manifest clinically, promoting proactive management and reducing the risk of complications.